EHC stands for electrochemical hydrogen compressor. This promising technology outperforms the most common hydrogen compression methods used today, such as the Reciprocating Hydrogen Compressor, where a piston compresses hydrogen inside cylinders, and the Diaphragm Hydrogen Compressor, where a flexible metal diaphragm compresses the gas without direct contact. Unlike these mechanical systems, EHC works without pistons or diaphragms, which significantly reduces mechanical wear and maintenance effort.
Global investigation into Electrochemical Hydrogen Compression EHC
Electrochemical hydrogen compression is a topic that has been studied extensively in the scientific community. Research from the USA, the Netherlands, Pakistan, Germany, Korea, and Mexico contributes to the understanding and continuous improvement of this technology.
Basics of hydrogen cell technologies
Fuel cells, electrolyzers, and electrochemical hydrogen compressors share many fundamental principles. Understanding these basics is essential for understanding EHC systems.
How does a hydrogen fuel cell work
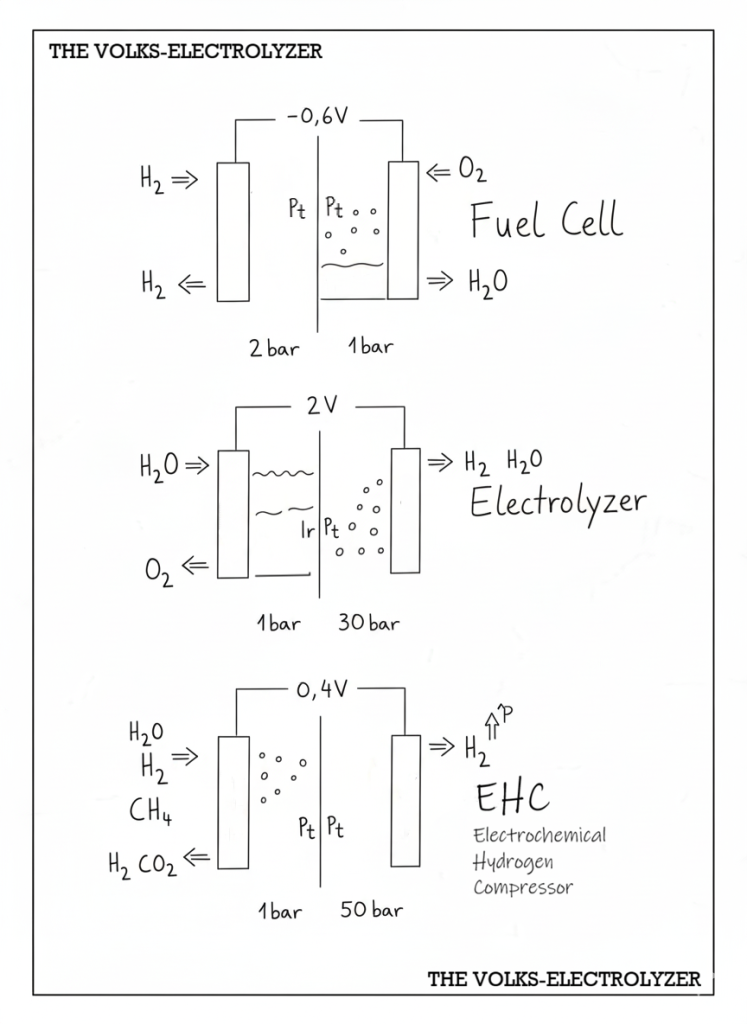
A hydrogen fuel cell consists of an anode and a cathode separated by a membrane. A flow field distributes the gases across the cell surface. Hydrogen enters one side, electricity is produced, and oxygen from the surrounding air reacts on the other side. A single fuel cell produces approximately 0.6 volts. The outputs are electrical energy and a mixture of water vapor and liquid water. Platinum catalysts are used on both sides, typically together with a Nafion proton exchange membrane.
How does an electrolyzer work
An electrolyzer consists of many cells with anodes and cathodes separated by a membrane. Water is supplied to the system. Iridium is used as a catalyst on the oxygen side, while platinum is used on the hydrogen side. Oxygen exits at approximately ambient pressure, while hydrogen typically exits at around 30 bar, together with water vapor. As a rule of thumb, applying about two volts per cell splits water into hydrogen and oxygen.
How does electrochemical hydrogen compression work?
Electrochemical hydrogen compression again uses an anode, a cathode, and a membrane with platinum catalysts. This time, hydrogen is supplied instead of water. The system operates at approximately 0.4 to 0.5 volts per cell. Hydrogen molecules are split into protons and electrons. Protons pass through the membrane and recombine on the other side, producing hydrogen at higher pressure. Typical pressure increases reach up to 50 bar per stage, often starting from 30 bar when hydrogen is supplied directly from an electrolyzer. This process also results in hydrogen purification.
EHC Electrochemical hydrogen compressors – lower the maintenance cost
One of the key advantages of electrochemical hydrogen compressors is that they have no moving parts. While fuel cells and electrolyzers release heat, electrochemical hydrogen compression operates close to isothermal conditions. In contrast, piston-based hydrogen compressors are strongly exothermal and require active cooling. The near-isothermal behavior of EHC systems reduces thermal stress and maintenance requirements.
Where is the research on electrochemical hydrogen compression in 2026
Research focuses on single-cell behavior, membrane transport, flow field design, and back diffusion. Back diffusion becomes particularly important when large pressure differences exist, such as 50 bar on one side and 10 bar on the other. Flow field geometry, including meander-shaped channels, plays a critical role such as temperature and moisture management.
Multicell electrochemical hydrogen compressor in series and parallel
A single EHC cell consists of end plates, gaskets, current collectors, and a flow field. Because one membrane provides limited flow, multiple cells are combined. Parallel configurations increase flow at similar pressure, while series configurations allow much higher pressures at lower flow.
What membranes can be used in Electrochemical hydrogen compression
Thicker membranes reduce back diffusion but increase electrical resistance. Most systems use proton exchange membranes such as Nafion 212 or Nafion 117. These fluorinated polymers contain sulfonic acid groups, creating a highly acidic environment. As a result, catalysts and structural materials must be corrosion resistant.
Which companies sell electrochemical hydrogen compressors?
There are basically two companies commercializing EHC. The focus tumbles between purification of fossils and compression.
https://www.skyre-inc.com/
https://hyethydrogen.com/
At what temperature Electrochemical hydrogen compressors work and what pressures can be reached?
Electrochemical hydrogen compressors perform best at approximately 70 °C. Temperature regulation is therefore essential. Some experimental systems have reached pressures as high as 900 bar using large end plates and reinforced structures.
P&iD or Scheme of Electrochemical Hydrogen Compressor Systems
Water management is critical. Although the process itself does not require water, the membrane must remain hydrated. One effective approach is to feed moist hydrogen directly from an electrolyzer. Water traps can be used to control moisture, and excess water can be purged and returned to the electrolysis system.
Summary
Electrochemical Hydrogen Compression can be the missing link in the hydrogen economy. The company having an affordable EHC market ready will be able to compress hydrogen in any scale, thus be highly versatile. Hydrogen storage, Hydrogen appliances and Electrolyzers need compressors in order to have a acceptable energy density to replace fossil processes. We expect more companies rushing on this technology and optimizing real word chalenges, like efficiency and production costs. For the investors huge profits may come up in the future.
Videos werden nur für Mitglieder angezeigt.
Unterstützen Sie unsere Arbeit mit einer Mitgliedschaft. Vielen Dank!
Videos are only displayed for members.
Support our work by becoming a member. Thank you!
Les videos sont seulement visible pour les membres. Soutenez-nous en devenant membre. Merci beaucoup!
and check electrolyzer cost of more than 60 hydrogen manufacturers to see our best value